Contents
- Sine two angle addition formula
- Cosine two angle addition formula
- Sine double angle formula
- Cosine double angle formula
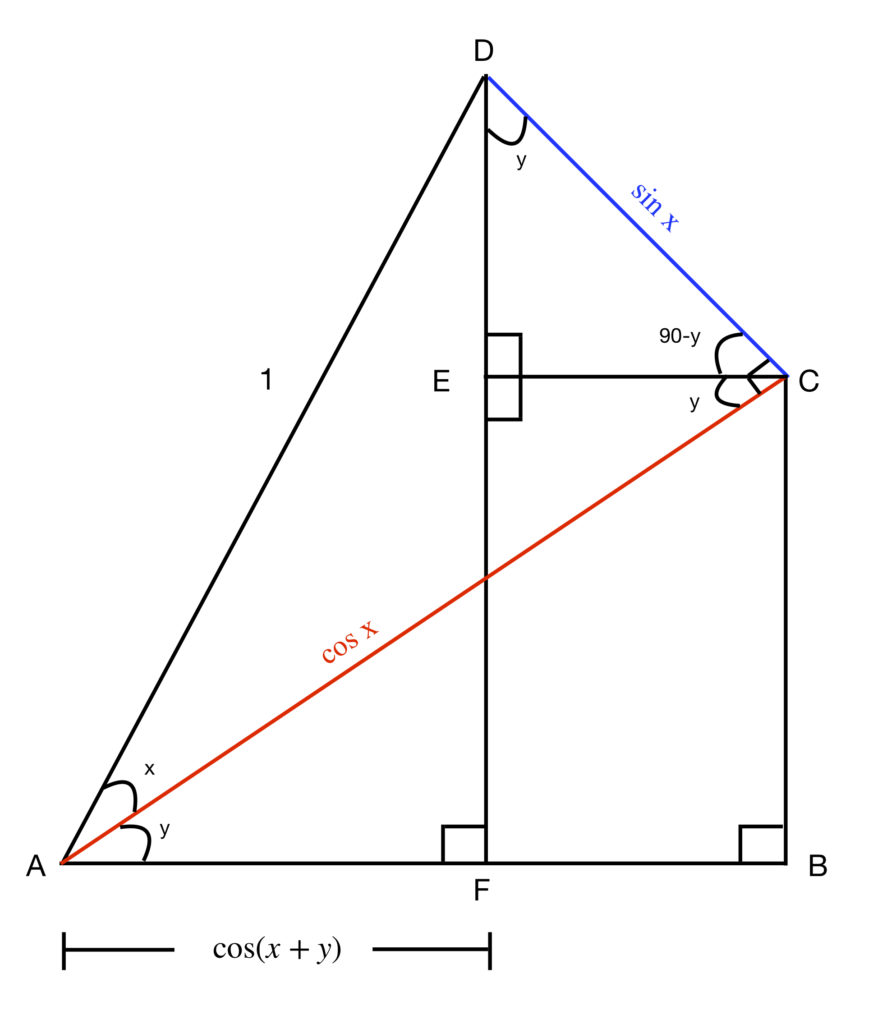
It may be useful to view the above diagram side-by-side with the following text. To do so, hold down the shift key and click on the figure. This will open the above figure in a new window. Once a new window is established, resize the current window and the new window with the figure in it so that both can be viewed simultaneously.
Sine two angle addition formula
We want to prove:
![]()
Looking at figure 1, note that
Cosine two angle addition formula
We want to prove
![]()
Looking at figure 1, note that
Sine double angle formula
We want to prove
![]()
From the sine two angle addition formula described above,
Cosine double angle formula
We want to prove
![]()
From the cosine two angle addition formula described above,
